+91 9150933557
SFS Super Food Spirulina
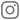
Superfoodspirulina is a safe food supplement which has richest protein source with powerful antioxident and modulate the immune system without side effects. Superfoodspirulina is a microscopic and filamentous cyanobacterium that derives its name from the spiral or helical nature of its filaments. Superfoodspirulina refers to the dried biomass of Arthrospira platensis, an osygenic photosynthetic bacterium found worldwide in fresh and marine waters. This alga represents and important staple diet in humans and has been used a source of protein and vitamin supplement in humans without side-effects. superfoodspirulina now belongs to the substances that are listed by the US Food and Drug Administration under the category Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS). It is relatively easy to cultivate but florishes only in alkaline lakes with an extremely high pH and in large outdoor ponds under controlled conditions. There are only a few areas worldwide that have the ideal sunny climate for production of alga, including Greece, Japan, India, United States and Spain.
Superfoodspirulina's Safety Clinical Evidence:-
Our Superfoodspirulina has been promoted as "the food of the future" with exceptional constituents that contribute to high energy levels. Superfoodspirulina increases healthy lactobacillus in the intestine, enabling the production of Vitamin B6 that also helps in energy release. Our Superfoodspirulina modulate the immune system by its role in covering nutritional deficiencies. Ramamoorthy and Premakumari in a more recent study administered superfoodspirulina supplements in ischemic heart disease patients and found a reduction in blood cholesterol, triglycerides and LDL cholesterol and an increase in HDL cholesterol. superfoodspirulina is also recommended for diabetic patients.
Superfoodspirulina's Anti Cancer /Antioxidants / Anti Viral Evidence:-
A Combined antioxident and immune modulation characteristics of superfoodspirulina having possible mechanism of tumor destruction and hence play a role in cancer prevention. There was no rise in the serum concentration of retinal Bcarotene despite supplementation and concluded that other constituents within superfoodspirulina is responsible for the anticancer effects.
Millions of people in Bangladesh, India, Taiwan and Chile are consuming high concentration of arsenic through drinking water and are at risk of chronic arsenic poisoning for which there is no specific treatment. A placebo-controlled, double blind study was conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of superfoodspirulina extract plus zinc in the treatment of chronic arsenic poisoning. 41 patients with chronic arsenic poisoning were randomly treated by either placebo (17 patients) or spirulina extract (250 mg) plus zinc (2mg) (24 patients) twice daily for 16 weeks. Each patient was supplied with arsenic-safe drinking water by installing a locally made water filter at household level. spirulina extract plus zinc was evaluated by comparing changes in skin and hair, between and placebo- and spirulina extract plus zinc-teated groups. Results showed that spirulina extract plus zinc twice daily for 16 weeks are useful for the treatment of chronic arsenic poisoning with melanosis and keratosis.C-phycocyanin (CPC) is one of the major biliproteins of superfoodspirulina with antioxidant and radical scavenging properties. It is also known to exhibit anti-inflammatory and anticancer properties.
Superfoodspirulina - Endorsed by:-

References:-
- J.C. Dillon, A.P. Phuc and J.P. Dubacq, "Nutritional value of the alga Spirulina," World Review of Nutrition and Dietetics, vol.77, pp.32-46, 1995.
- L.M. Tarantino, "Agency Response Letter GRAS Notice No.GRN000127," FDA Home page, October 2003.
- M. Salazar, G. Chamorro, S. Salazar, and C. Steele, "Effect of Spirulina maxima consumption on reproductive and peri- and postnatal development in rats," Food and Chemical Toxicology, pp. 353-359, 1996.
- G. Chamorro, S. Salazar, L. Favila-Castillo, C. Steele, and M.Salazar, "Reproductive and peri- and postnatal evaluation of spirulina maxima in mice,"Journal of Applied Phycology, vol.9, no. 2, pp. 107-112, 1997.
- M. Salazar, E. Martinez, E. Madrigal, L. E. Ruiz, and G.A. Chamorro, "Subchronic toxicity study in mice fed Spirulina," journal of Ethnopharmacology, vol. 62, no.3, pp. 235-241, 1998.
- A. Belay, "The potential application of Spirulina (Arthrospira) as a nutritional and therapeutic supplement in Health management," Journal of the American Nutraceutical Association, vol. 5, pp. 27-48, 2002.
- R. A. Kay, "Microalgae as food and supplement," Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, vol. 30, no. 6, pp. 555-573, 1991.
- C. Baicus and A. Baicus, "Spirulina did not ameliorate idiopathic chronic fatigue in four N-of-1 randomized controlled trials," Phytotherapy Research, vol. 21, no.6, pp. 570- 573, 2007.
- H.-N. Yang, E.-H. Lee, and H.-M. Kim, "spirulina platensis inhibits anaphaylactic reaction," :Life Sciences, vol. 61, no. 13, pp. 1237-1244, 1997.
- H.-M. Kim, E.-H Lee, H.-H. Cho, and Y.H. Moon, "Inhibitory effect of mast cell- mediated immediate-type allergic reactions in rats by Spirulina," Biochemical Pharmacology, vol. 55, no. 7, pp. 1071-1076, 1998.
- T. K. Mao, J. van de Water, and M. E. Gershwin, "Effects of a Spirulina-based dietary supplement on cytokine production from allergic thinitis patients," Journal of Medicinal Food, vol.8, no. 1, pp. 27-30, 2005.
- K. Ishii, T.Katoch, Y. Okuwaki, and O. Hayashi, "Influence of dietary Spirulina platensis on IgA level in human saliva," Journal of Kagawa Nutrition University, vol. 30, pp. 27-33, 1999.
- T. Hirahashi, M. Matsumoto, K. Hazeki, Y. Saiki, M. Ui, and T. Seua, "Activatino of the human innate immune system by Spirulina: augmentation of interferon production and NK cycotoxicity by oral administration of hot water extract of Spirulina platensis," International Immunopharmacology, vol.2, no. 4, pp. 423-434, 2002.
- C. Cingi, M. Conk-Dalay, H. Cakli, and C. Bal, "The effects of spirulina and allergic thinitis," European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology. In press.
- K. Hayashi. T. Hayashi, M. Maedaa, and I.Kojima, "Calcium spirulan, an inhibitor of envelope virus replication, from a blue-green alga Spirulina platensis," Journal of Natural Products, vol. 5, pp.83-7, 1996.
- S. Ayehunie, A. Belay, T.W. Baba, and R.M. Ruprecht, "Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by an aqueous extract of Spirulina platensis (Arthrospira platensis)," Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes and Human Retrovirology, vol. 18, no. 1, pp. 7-12,1998.
- N. Nakaya, Y. Homa, and Y.Goto, "Cholesterol lowering effect of Spirulina," Atherosclerosis, vol. 37, pp. 1329-1337, 1998.
- A. Ramamoorthy and S. Premakumari, "Effect of supplementation of Spirulina on hypercholesterolemic patients," Journal of Food aScience and Technology, vol. 33, no. 2, pp. 124-128, 1996.
- U. V. Mani, S. Desai, and U. Iyer, "Studies on the long term effect of Spirulina supplementation on serum lipid profile and glycated proteins in NIDDM patients," Journal of Nutraceuticals, Fuctional and Medical Foods, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 25-32, 2000.
- B. Mathew, R. Sankaranarayanan, P.P. Nair et al., "Evaluation of chemoprevention of oral cancer with Spirulina fusiformis," Nutrition and Cancer, vol.24, no. 2, pp. 197-202, 1995.
- G. Shklar and J. Schwartz, "Tumor necrosis factor in experimental cancer regression with alphatocopherol, beta-caratene, canthoxanthin and algae extract," European Journal of Cancer and Clinical Oncology, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 839-850, 1988.
- J.Schwartz, G.Shklar, S.Reid, and D.Trickler, "Prevention of experimental oral cancer by extracts of Spirulina- Dunaliella algae," Nutrition and Cancer ,vol.45,no.6,pp.510- 515,1987.